Rooting your Android phone grants freedom, bypassing manufacturer restrictions. But beware, it can expose your device to security threats. While rooting lets you remove unwanted apps and install anything you desire, it can also void your warranty and potentially harm your device.
So, what exactly is rooting, and are the risks worth the benefits? Let’s explore both sides.
What is rooting?
Rooting is the act of accessing and modifying the root directory of an Android device’s operating system. Manufacturers and carriers usually restrict access to root files to prevent users from harming their devices.
A rooted Android device offers complete customization but with all the associated risks and dangers. To root a device sounds like complicated technical wizardry, but to root a device, you simply gain full system administrator permissions.
Android is based on a Unix-like operating system, in which the final system admin account is called “root”. By gaining unrestricted access to all system folder locations, folders, and commands on your Android device, you essentially become the root.
For most people, rooting a phone isn’t worth the risk, especially considering the power and versatility of today’s smartphones.
Just like jailbreaking your iOS device, rooting your Android phone removes all the safeguards and voids your warranty, which is why you should never root an Android phone unless you know exactly what you are doing.
Rooting your Android phone unlocks some features, but it’s too easy to cause serious damage to a rooted phone, and your data is especially sensitive if hackers discover your lost phone.
So, is Root Access Worth It? First, you need to understand what is Root and what is a Rooted Android device. Then, you need to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of Rooting your Android phone.

The risks of rooting Android devices
Whether you are a business, journalist, activist, or dissident, you may need to have root access to modify the device’s functionality or install custom software.
However, having root access comes with its own set of risks and drawbacks, and in most cases, the downsides of heavily rooting an Android phone far outweigh the advantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons of rooting your Android phone.
Benefits of Rooting Android Devices
People root Android devices for several reasons:
- Customization
- Removing Bloatware
- Access to root-only apps
- Performance tweaks
- Backup and Restore
- Wi-Fi and Tethering
- Ad Blocking
Customization
Rooting your phone lets you be the boss of it! Normally, phones don’t let you change too much stuff because it might mess things up. But if you’re careful, rooting lets you change things like colors and pictures to make your phone look exactly how you want.
It also lets you use special programs that can make your phone work faster or do new things.
Removing Bloatware
Rooting your phone lets you get rid of those annoying extra apps that come on the phone already. These are called “bloatware” and they take up space and slow your phone down.
Rooting lets you take them out, just like throwing away trash, to free up space for things you want. This can make your phone work better and have more room for your stuff.
Access to Root-only Apps
Some apps require root access to unlock additional features or access system-level settings. Rooting allows users to install and use these apps.
Performance Tweaks
Rooting provides access to system settings and files that are otherwise inaccessible. This allows users to tweak settings to optimize performance, such as overclocking the CPU or adjusting system animations.
Backup and Restore
Normally, your phone picks a spot to store your backups, but you can’t change it. Rooting lets you be the boss of your backups too! You can pick a different spot, like a memory card, to keep your important stuff safe. This can be helpful if your phone ever breaks or you get a new one.
Wi-Fi and Tethering
Rooting can enable features like Wi-Fi tethering, which allows users to share their device’s internet connection with other devices, without requiring carrier permission.
Ad Blocking
Rooting can enable ad-blocking at the system level, blocking ads in apps and browsers without the need for separate ad-blocking software.
Disadvantages of rooting an Android device
Rooting an Android device unlocks a treasure trove of potential, but it’s not without its dangers. Here’s a breakdown of the key risks to consider:
- Security Vulnerability
- Warranty Voiding
- Bricking Risk
- Unstable Performance
- Banking App Issues
- Pirated App Peril
Security Vulnerability
Rooting bypasses security measures put in place by manufacturers, making your device more susceptible to malware attacks. With root access, malicious apps can wreak havoc on your system.
Warranty Voiding
Rooting typically violates your device’s warranty. If something goes wrong after rooting, the manufacturer might not offer repairs or replacements under warranty.
Bricking Risk
Messing up during the rooting process can “brick” your device, rendering it completely unusable. This can be a permanent situation, leaving you with a fancy paperweight.
Unstable Performance
Rooting can lead to software instability, causing crashes, freezes, and unexpected behavior on your phone.
Banking App Issues
Some banking and financial apps have built-in security features that detect rooting and stop functioning to protect your financial information.
Pirated App Peril
Rooting might seem like an invitation to download pirated apps, but these sources are often riddled with malware and pose a significant security risk.
How to root your Android device
Rooting methods can vary depending on the device model, manufacturer, and Android version. Here’s a general outline of the steps involved in rooting an Android device:
Backup Your Data
Before you begin, it’s crucial to back up your device data, including contacts, photos, videos, and any important files, as the rooting process may result in data loss or device malfunction.
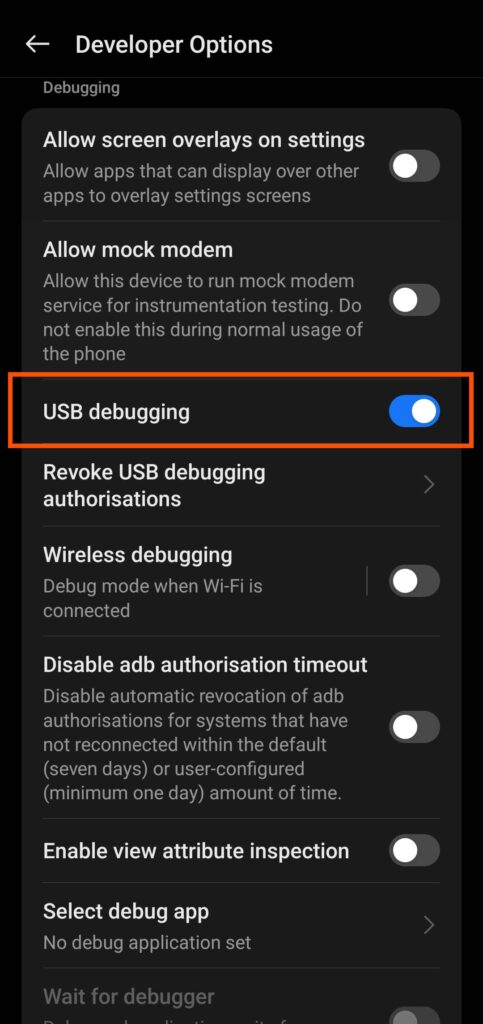
Enable USB Debugging
Go to your device’s Settings, then to Developer Options (if available), and enable USB debugging. This allows your computer to communicate with your device during the rooting process.
Unlock Bootloader (if necessary)
Some devices require unlocking the bootloader before rooting. This process varies depending on the device manufacturer. You’ll typically need to visit the manufacturer’s website and follow their instructions for unlocking the bootloader.
Download Rooting Software
There are various rooting tools available, such as Magisk, SuperSU, and KingoRoot. Download the appropriate rooting software for your device and transfer it to your device’s internal storage.
Install Custom Recovery (optional)
Installing a custom recovery like TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project) can make the rooting process easier and provide additional functionality. You can usually find instructions for installing TWRP for your device on XDA Developers forums or other Android enthusiast websites.
Root Your Device
The exact steps for rooting your device will depend on the rooting method you choose. Generally, you’ll need to boot your device into recovery mode, select the option to install the rooting software from the internal storage or SD card, and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the rooting process.
Verify Root Access
Once the rooting process is complete, you can verify that your device has been successfully rooted by installing a root checker app from the Google Play Store.
Customize and Manage Root Access
After rooting, you can customize your device further by installing custom ROMs, tweaking system settings, and using root-only apps. You can also manage root access for individual apps using apps like Magisk Manager.
For most folks, the potential dangers of rooting outweigh the benefits, especially considering how powerful and customizable modern smartphones already are. We strongly advise against rooting unless you’re certain about what you’re doing and have a full backup of your data.
If you’re determined to root your device, be prepared to delve into some technical settings. First, enable “developer mode” by tapping your phone’s build number seven times within the “About Phone” section of settings. This unlocks “Developer Options” where you’ll need to turn on “OEM Unlocking” and “USB Debugging.”
The specifics will vary depending on your device, but here’s a general overview of the rooting process once you’ve enabled those options:
- Unlock the Bootloader: This program initiates your phone’s startup. Manufacturers like Google and Motorola might allow official unlocking, but it could still void your warranty depending on your carrier.
- Flash a Custom ROM: After unlocking the bootloader, you can overwrite your device’s stock operating system with a custom one.
- Third-Party Software (Use Wisely): You’ll likely need extra software to finalize the rooting process. Look for programs that perform a “systemless root” without modifying core system files. Be very cautious of tools that promise one-click rooting, as these are often malware traps. If you suspect you’ve been tricked, take immediate steps to remove spyware from your Android device.
Troubleshooting rooting issues
If your rooting adventure went awry and your phone is now “bricked” (completely unusable) or experiencing other issues, here are some Hail Mary attempts to potentially revive it. However, extreme caution is advised, as these steps can further damage your device if not done correctly.
- Boot into Recovery Mode: This is a special mode separate from the normal Android system, allowing you to perform basic troubleshooting tasks. The method to enter recovery mode varies greatly between phone brands. Thankfully, the XDA Developers community (https://www.xda-developers.com/) has a handy guide that explains how to access recovery mode for different Android models.
- Clear the Cache Partition (Risky): This option removes temporary system files that might be causing problems. Be aware, though, that the wording might be confusing. Sometimes this option might be labeled “wipe all data” or something similar. Double and triple-check what you’re selecting before proceeding, as wiping all data will erase everything on your phone!
- Reboot and Assess: After clearing the cache, restart your phone and see if the rooting issue is resolved. There’s a chance this might clear up minor glitches.
- Factory Reset (Nuclear Option): If clearing the cache fails, you can attempt a factory reset, which wipes your entire phone clean and restores it to its original factory settings. This will erase all your data, apps, photos, and everything else, so make sure you have a complete backup before going down this route.
- Reinstalling the Operating System (For Tech-Savvy Users Only!): This is the last resort and should only be attempted by users with significant technical expertise. It involves connecting your phone to a computer, flashing it (rewriting its operating system), and installing either the original operating system provided by your manufacturer (stock ROM) or a custom ROM. Improper flashing can permanently damage your phone, so make sure you have the right software, files, and instructions specific to your device model before attempting this.
If you’re uncomfortable with any of these steps or don’t possess the technical knowledge, it’s strongly recommended to seek help from a professional to avoid further damaging your phone.
Is rooting legal and safe?
Rooting is perfectly legal in the US.
Rooting itself is generally considered legal. In the US, there’s a law called the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) that has an exemption allowing users to bypass certain security measures on devices they own to achieve lawful purposes.
Rooting can fall under this exemption because it allows you more control over your device.
However, there are important safety considerations to keep in mind:
- Warranty: Rooting almost always voids your device’s warranty. This means if your phone malfunctions after rooting, the manufacturer likely won’t fix it for free.
- Security Risks: Rooting bypasses security measures put in place by the manufacturer. This can make your device more susceptible to malware attacks and other security threats.
- Bricking Risk: The rooting process can be complex, and if done incorrectly, it can “brick” your device, rendering it completely unusable.
In summary, rooting is legal but not necessarily safe. It’s best to weigh the potential benefits (customization, advanced features) against the risks (warranty voiding, security vulnerabilities, bricking) before deciding if it’s the right choice for you.
Read Also:
How to Download Voice Messages on Instagram on Mobile Phone & PC? (techkick.in)
How to take Screenshots on Windows in 2024 (tech kick.in)
Should you root your Android device?
Rooting your phone isn’t recommended for a variety of reasons, including security concerns and the potential to compromise your device’s performance. It’s also highly unlikely that rooting your phone will invalidate your warranty.
There are some legitimate reasons for people to root their Android devices. Whistleblowers and journalists may wish to configure an ‘untraceable’ phone, for example. Software engineers may also need an unlocked device for testing. But for the majority of people, rooting is simply not necessary or recommended.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to root your Android device depends on your technical expertise, comfort level with risk, and what you want to achieve with your phone. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide.
The Verdict?
If you’re a casual user who values stability, security, and a functioning warranty, then rooting is probably not for you. The benefits likely won’t outweigh the risks.
However, if you’re an experienced user who is comfortable with technical procedures, understands the risks involved, and has a specific reason for wanting to root (like installing a custom ROM or gaining access to advanced features), then rooting might be an option to consider. Just proceed with caution, do your research specific to your device model, and have a full backup ready in case something goes wrong.
Does rooting a phone void the warranty?
In most cases, yes, rooting your Android phone will void the warranty. This is because rooting bypasses security measures and restrictions put in place by the manufacturer.
When something goes wrong after rooting, the manufacturer can often point to the rooting process as the cause and deny warranty coverage for repairs or replacements.
It’s important to understand that warranty policies can vary depending on your location and specific device. While rooting almost always voids the warranty, there are a few exceptions. For instance, in the European Union, a law protects consumers’ rights to a minimum two-year warranty on electronic devices.
This law doesn’t allow manufacturers to void the warranty solely because a device is rooted, as long as the root cause of the issue isn’t directly related to rooting.
However, even in the EU, manufacturers might still try to weasel out-of-warranty repairs if your device is rooted. The onus would be on you to prove that the root cause of the problem wasn’t the rooting process.
So, to answer your question definitively: rooting your phone very likely voids the warranty, but there can be some exceptions depending on your location and specific circumstances.
It’s always best to check your device’s warranty policy or contact the manufacturer directly before rooting to know for sure what the implications will be.
Conclusion
Rooting your phone gives you more control over it, like picking cool colors, getting rid of those extra apps you don’t want, and even choosing where to store your important stuff. It can also free up space on your phone and make it work faster.
But be careful when rooting because it can be a bit tricky. If you’re not sure what you’re doing, it’s best to ask someone who knows more about it.


Good day! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I truly enjoy reading through your articles. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same subjects? Thanks for your time!
Thanks a lot. Yes, you can visit my site techkick.in. You get lot of blogs that really helps you.
Another thing is that while looking for a good on the net electronics retail outlet, look for web stores that are continuously updated, trying to keep up-to-date with the latest products, the top deals, and helpful information on products. This will make sure that you are getting through a shop which stays on top of the competition and gives you what you should need to make knowledgeable, well-informed electronics buys. Thanks for the crucial tips I’ve learned through your blog.
Welcome Friend.
You’re so skilled!
Thanks.😀
Your writing style is engaging and informative. I’ve learned so much from this post and can’t wait to apply these tips to my own projects.
Thank you😊
Thank you for this comprehensive guide. The practical tips you’ve shared are going to be very useful for my work.
I learned a lot from this article.
😊
Spot on with this write-up, I truly think this web site wants much more consideration. I’ll in all probability be once more to read way more, thanks for that info.