Forget about speedy apps or multitasking – without lightning-fast data storage and retrieval, your computer would grind to a halt.
That’s where RAM steps in as your system’s superstar. But what exactly is RAM, and how does it keep things running smoothly?
This guide will break down the meaning of RAM, explain why it’s crucial for speedy performance, and even offer tips on optimizing your computer’s RAM with specialized software.
What is RAM on a computer?
Imagine your computer’s brain. RAM acts as its short-term memory, holding information the processor needs. Unlike long-term storage (like a hard drive), RAM allows super-fast access to this data, making it essential for a smooth-running system.
What does RAM stand for?
RAM, short for random access memory, is the workhorse behind almost every computing device. Imagine it as a special kind of super-fast notepad for your computer, constantly refreshed with only the information it needs at that exact moment.
This temporary storage acts like an express lane for the processor, allowing it to grab data instantly without waiting for slower long-term storage to churn.
Whether you’re editing a photo on your phone, browsing the web on your laptop, or streaming a movie on your smart TV, all devices rely on RAM for those active tasks.
Even though they also have long-term storage like hard drives or solid-state drives to hold onto files and information you need to keep, RAM is the key to keeping things running smoothly in the present moment.
What does computer memory (RAM) do?
Imagine your computer’s memory like a workspace. Picture your desk overflowing with papers, folders, and half-empty coffee mugs – that’s how a hard drive can get with all the documents, photos, music, and videos you accumulate over time.
It’s like an attic or a cluttered basement, storing everything you might need someday but don’t necessarily use regularly.
RAM, on the other hand, is the equivalent of a clean, organized desk blotter. It’s a dedicated area specifically for the things you’re actively using, like the document you’re editing or the website you’re browsing.
This allows instant access to information, just like grabbing a pen from your desk instead of diving under a pile of papers to find one.
Less-used stuff, like old tax files or downloaded movies, gets shoved into drawers or filing cabinets, which function like your computer’s hard drive.
You can also think of cloud storage as an off-site filing facility – it holds the information you need to keep but don’t use regularly, and accessing it takes a bit longer than grabbing something from your desk. It’s like keeping important documents in a secure storage locker instead of cluttering up your home office.
What is RAM used for?
RAM is used to store and retrieve information immediately. RAM can process information much faster than what is stored on a hard disk, up to 20 to 100 times faster depending on the hardware and the task.
When a program like Microsoft Word is opened, the computer loads the program into RAM. When the program is done actively working with the program, the computer converts the program back into RAM.
If you open a document that you already saved on your computer, the operating system will find the file in long-term storage and copy the information onto RAM. Since RAM is so fast, once the data is in RAM, you get almost immediate performance.
When a document or other type of file is saved, the data is copied to the hard drive or another long-term memory. When an application is closed, the operating system extracts memory from the RAM, freeing up space in the computer’s short-term memory to work on the next project.
If, for example, a document is forgotten to save to the hard drive and the computer’s power fails, all of that work is lost because RAM is only meant for temporary storage.
RAM is used to store and retrieve data in real-time. It can be used for any purpose that requires fast access to computing power.
Another use of RAM is to speed up the loading of previously accessed information. For example, when you first boot your computer and start an application, like PowerPoint or Spotify.
It takes a while for the application to load, but if you close the program and then start it again, the application will open almost immediately (especially if you have an optimized PC).
This is because the data required to load the application is stored in RAM, which is much faster than the hard drive. RAM is used for anything that requires fast access to computational resources.
For example, Windows feature SuperFetch automatically pre-loads applications and files in RAM based on a user’s behavior. SuperFetch records the user’s usage patterns and then automatically loads the application or file into RAM.
CPU vs RAM, Which one is better?
The CPU (central processing unit) is the brain of your computer. It does all the calculations needed to run software programs. But for the CPU to run smoothly and efficiently, it needs RAM to provide it with high-speed data access. It is a joint effort between the CPU and RAM.
So while both are important components, upgrading or overclock your CPU will increase raw processing power if you want to optimize PC performance. This will help you run more resource-intensive programs and handle bigger multitasking workloads.
Increasing RAM capacity will primarily allow you to run faster, more complex processes.
How much memory do I need?
The more RAM you have, the faster your computer will run. However, if you have an old device, you may need to update the RAM or some other hardware. All open applications (including your browser tabs) use RAM.
When your RAM runs out, your computer will have to move things to free up some space on your hard disk. This causes your computer to slow down. RAM differs from storage in that if you turn your PC off, the information stored in your RAM will be lost, while the data stored in your long-term memory (SSD/HDD) will be preserved.
How much RAM I need depends on my usage of apps and programs, the number of applications I have open at any given time, and my level of patience. We expect our devices to be able to respond to our commands in no time.
If you notice that your computer is not running as fast as it could, you should check your RAM, and other PC specs, and make sure you are not overloading your computer.
Most of the time, you don’t need nearly as much RAM as hard disk space. Think about your desk at home, the more space you have, the more paper you can spread out. But you might still need a large filing cabinet to house all your accumulated documents.
In the early days of the Pentium-powered computer, you didn’t usually need more than 8 MB of RAM — maybe 32MB if you were a real tech nut.
Nowadays, a web browser loaded with multiple tabs can consume more than 2.2GB RAM.
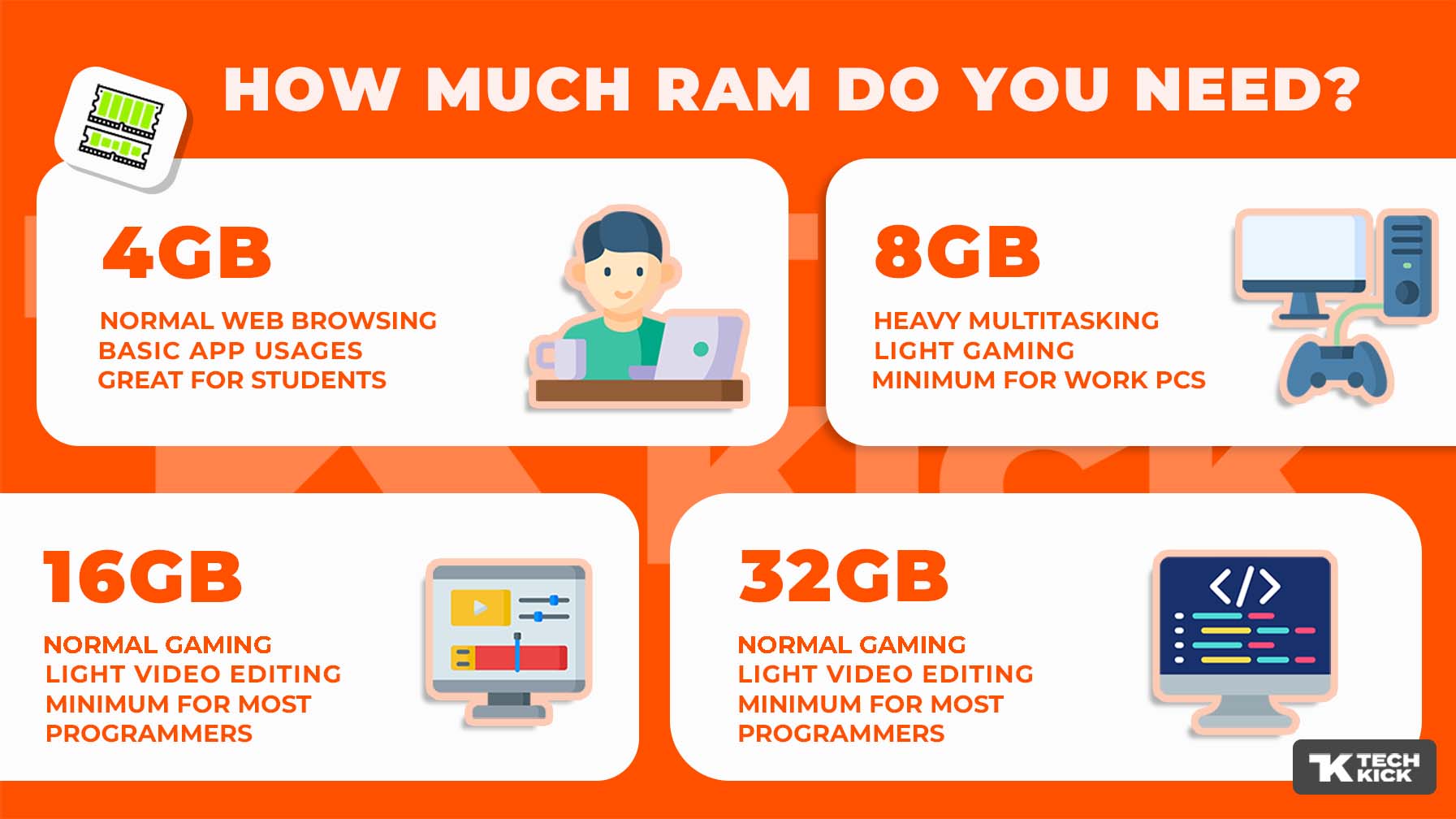
When you purchase a computer, there are four RAM options available: 4GB RAM, 8GB RAM, 16GB RAM, and 32GB RAM (or 64GB RAM if you use premium editing software or play a lot of games).
Most entry-level or legacy devices come with 4GB RAM, while more expensive machines have either 8GB RAM or 16GB RAM, and you can find even more RAM on professional-level computers. How much RAM do you need, and for what?
Here are our recommendations for any operating system and personal computer hardware.
- 4GB RAM: If you only use your computer for browsing the web, running standard Office applications, or doing light photo editing, then 4GB RAM should be sufficient.
- 8GB RAM: For heavy multitaskers and light gamers, 8GB of RAM should suffice.
- 16GB RAM: Some computing-intensive tasks require 16GB of RAM, such as high-end gaming, high-end video editing, high-end programming, or running multiple intensive tasks at the same time. Those who want professional-level performance without any slowdowns will want 16+GB RAM.
How do you know if you have enough RAM?
When the computing tasks on your computer exceed the available memory, the operating system must select an application and transfer it to the hard disk. When you return to that application, the operating system needs to retrieve the information from the hard drive before you can use it. This process is known as paging or swapping. It takes a lot of time and slows down your computer.
One way to improve your computer’s performance is to regularly clear your RAM of wasteful clutter. This can be done manually, but a specialized software tool can make it easier.
What are the types of RAM?
Yes, there are different types of RAM. Like other types of computer hardware, RAM is constantly being developed to reduce power consumption while simultaneously increasing speed and memory capacity.
RAMs have been around since the very early days of computing. In the early days of microcomputing, enthusiasts had to plug in the RAM chips one by one.
The main types of RAM in the late 1980s and early 1990s were SRAM or Static RAM, DRAM or Dynamic RAM, and SDRAM or Synchronous Dynamic RAM.
Nowadays, the most popular type of RAM is DDR-SDRAM or Double data rate Synchronous dynamic random-access memory.
There are several versions of DDR-DDRRAM, including DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. DDR (Double-Data Rate) RAM allows for multiple file transfers at the same time. The latest version, DDR5-RAM, has a data rate of 51.2 GB/s.
Due to supply-chain issues, DDR5 is difficult to obtain — and very expensive.
DDR4 is still the most popular type of RAM, but it also comes in a variety of types and speeds. Most DDR4 memory sticks run at 2,400MHz or higher. To get the maximum performance out of the memory, you can opt for higher-clocked RAM, from 3,200 MHz to 5,000 MHz (important for gamers and GPU overclocks). The higher the MHz, the faster your RAM will run.
VRAM is also known as Video Random Access Memory (VRAM). It is used in the graphics card to process graphical data while playing games, editing photos, or performing other graphics-intensive tasks.
Video RAM is faster than regular memory, and is usually found in the form of “Graphics Double Data Rate” or “GDDR” memory, which is a particular type of memory that is optimized for graphic rendering. The most recent generation — “GDDR6” — has a total data rate of 72 Gbps.
Some high-end graphics cards also use another type of memory, called “HBM” or High Bandwidth Memory, which is hard to come by and certainly not cheap.
| RAM type | Speed | Bandwidth |
| DDR2 | 533-800 MHz | 4.27-6.4 GB/s |
| DDR3 | 1066-1866 MHz | 8.5-14.9 GB/s |
| DDR4 | 2133-3200 MHz | 17-25.6 GB/s |
| DDR5 | 3200-8400 MHz | 38.4-51.2 GB/s |
| GDDR6 | 3000-3600 MHz | 64-72 GB/s |
| HBM | 6400 MHz | 128-410 GB/s |
DRAM vs SRAM
SRAM stands for Simple Residual Memory, and DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. They both use different technologies to store data. SRAM relies on transistors that store memory as long as it receives a constant flow of power.
DRAM, on the other hand, relies on capacitors that must be “recharged” by relatively large bursts of power every few milliseconds. While SRAM technology is much smaller, faster, and energy-efficient, it is also much more expensive than DRAM technology.
This is why SRAM is often used for cache memory and DRAM is typically used in the main memory of a computer. Today, the most popular form of DRAM used in modern computers is called synchronous DRAM or SDRAM, which stands for Simple Random Access Memory.
SDRAMs are much faster than traditional DRAMs, but they still consume a lot of power.
What is ROM?
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of memory on a computer that can be read but not written to. This type of memory is commonly used for storing and playing music (CDs) or films (DVDs). In contrast to RAM, a computer cannot write new data to ROM, only reads it or plays it back.
What is the best way to get more RAM without having to upgrade?
If you are having trouble with low PC performance or your computer has RAM of 4GB or less, then the best way to increase computing speed without purchasing a new machine is by freeing up your RAM.
There are two ways to free up RAM without upgrading RAM cartridges.
First, close active programs. All browser tabs, especially in Chrome, and applications you are running consume RAM. If you do not need a tab or you are not actively using an application, close it and only launch what you are using.
Second, use Sleep Mode.
If you are having trouble with low PC performance or your computer has RAM of 4GB or less, then the best way to increase computing speed without purchasing a new machine is by freeing up your RAM.
There are two ways to free up RAM without upgrading RAM cartridges.
First, close active programs. All browser tabs, especially in Chrome, and applications you are running consume RAM. If you do not need a tab or you are not actively using an application, close it and only launch what you are using.
What should I look out for when buying RAM?
The most recent generation of DDR4 RAM clocks in at about 2,400MHz for most users. Gamers, on the other hand, will want DDR4 RAM that operates at about 3,200MHz on Intel chips and around 3,600MHz on AMD chips.
Professional programmers, multimedia editors, and hardcore gamers may want higher-clocked DDR4 RAM with speeds as high as 4,800MHz on G.Skill or 4,400MHz on Corsair. While clock speeds are important, another factor to consider is latency.
Latency is the time difference between when a command is entered in memory and when it is executed. The lower your latency, the better your performance. For high-level performance, you will need DDR4 RAM that clocks in at least 4,000MHz and has a latency of about CAS 15-18 or lower.
When you buy DDR4 RAM, you may see it listed as CL 16, which stands for “Column Latency 16.” This won’t make much of a difference to regular users, but gamers should keep an eye out for it.
If you’re planning to upgrade your Mac’s RAM, make sure it’s possible to add it to your model before.
Please Note the 32-bit Windows versions
At the end of the day, you can’t just install an infinite amount of RAM on your PC and hope for the best. If you want to use more RAM than 4GB, you’ll need to run 64-bit versions of Windows (32-bit versions only have 3.5 GB of RAM). If you’re still using Windows 7’s 32-bit version, you’ll have to upgrade to Windows 11’s 64-bit to get 4GB or more RAM.
However, it’s important to note that installing 64-bit on an older machine with less RAM may have an adverse effect. Windows now uses 64 bits of address space instead of 32 bits, which means that each application takes up 20% to 50% more memory depending on which apps you use. So, it only makes sense to run Windows in 64-bit if you have more system memory.
RAM and Gaming
The RAM requirement depends on the requirements of the game you are playing, the required graphical quality and resolution, and whether you are going to multitask or run background apps. In general, games that are more demanding and have higher resolutions will need more RAM.
For instance, games such as Fortnite, League of Legends, and PUBG (Player Unknown’s Battlegrounds: BattleGrounds) have a minimum memory requirement of 2GB, 4GB, and 6GB respectively.
If you have more RAM than the minimum requirement, you will be able to play games more smoothly and with higher FPS. However, after a certain point in time, adding more RAM will not provide you with additional performance boosts. Therefore, you should check the average FPS of your games to see if you need to upgrade.


Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
You can definitely see your expertise in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
I have really noticed that repairing credit activity should be conducted with techniques. If not, chances are you’ll find yourself causing harm to your positioning. In order to grow into success fixing your credit ranking you have to make sure that from this moment you pay any monthly costs promptly in advance of their booked date. It is really significant on the grounds that by not necessarily accomplishing that area, all other moves that you will decide on to improve your credit position will not be powerful. Thanks for giving your thoughts.